Maritime Robotics – Future of Autonomous Ships
The Future of Autonomous ShipsThe Future of Autonomous Ships
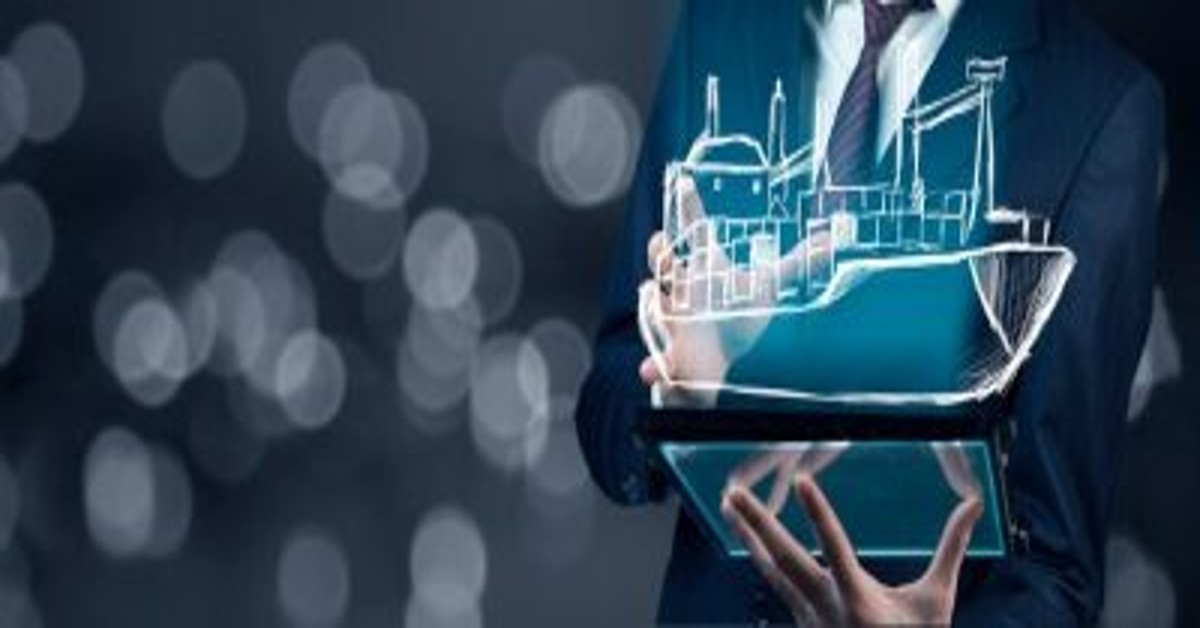 The Future of Autonomous Ships – We live in an age where our roads are poised to be overrun by driverless cars from technology giants like Tesla, Google, and Uber. But what about our navigation in the mighty seas? Autonomous robotics have been becoming popular in the shipping industry for a while. However, global adoption and long-term sustainable solutions are currently setting the shipping industry back from creating a truly . But many shipping giants are recognizing the importance of integrating semi or semi-autonomous solutions into their portfolio. Automation will make the shipping industry more cost and energy-efficient, reduce accidents and even reduce the threat of piracy!
The Future of Autonomous Ships – We live in an age where our roads are poised to be overrun by driverless cars from technology giants like Tesla, Google, and Uber. But what about our navigation in the mighty seas? Autonomous robotics have been becoming popular in the shipping industry for a while. However, global adoption and long-term sustainable solutions are currently setting the shipping industry back from creating a truly . But many shipping giants are recognizing the importance of integrating semi or semi-autonomous solutions into their portfolio. Automation will make the shipping industry more cost and energy-efficient, reduce accidents and even reduce the threat of piracy!
Semi-autonomous solutions – The Future of Autonomous Ships
The shipping industry is complex and enormous, making it difficult to adopt hardware innovations globally. Introducing autonomous systems requires a step-by-step approach rather than an all-or-nothing solution. The purpose, after all, is to optimize the system for less work on board, better performance, and less human error.
So, one of the most viable options available is to retrofit exiting ships with autonomous technologies. For example, San Francisco-based start-up Shone provides piloting assistance and movement prediction services. This semi-autonomous solution helps delegates the predictive analysis of other vessels from the crew to the autonomous technology.
Many ships already have remote control systems that can work without the presence of humans. Humans operate such semi-autonomous ships remotely from the shore.
The natural progression to this will be completely autonomous and remote solutions. Rolls-Royce has partnered with Svitzer to develop the world’s first remotely operated commercial vessel in Denmark. Svitzer’s Hermod tug has already conducted many remotely operated trips manned by the caption located at the Svitzer base.
Autonomous solutions
Rolls-Royce and the Finnish ferry operator Finferries developed the world’s first fully autonomous ferry named Falco. This ferry uses IoT technology, which enables it to detect objects using sensors and analyze them with the help of AI. This autonomous ship can automatically alter its course and automatically reduce its speed upon reaching the destination without human intervention.
Yara Birkeland, a Norwegian container ship touted as the world’s first autonomous container ship, is close to full deployment. The company, Yara International, claims that this ship is a zero-emissions, electric vessel.
Wärtsilä has developed an Advanced Intelligent Maneuvering (AIM) system to be deployed in ports. This Smart navigation collision system helps ships to navigate efficiently and avoid all collision risks. Singapore’s IntelliTug project is using this advanced situational awareness system.
Companies shifting their focus to autonomous shipping have seen a growth spurt during the last few years. Recently, Kongsberg acquired the Rolls-Royce Commercial Maritime division. Samsung has created a Smart Shipping platform. The operations are based out of their Heavy Industries division. Crowley recently completed designing the first US electric tug. Things are picking up speed in the autonomous shipping industry!
Advantages of autonomous ships – The Future of Autonomous Ships
The future of Autonomous ships can improve the safety, efficiency, and quality of the work involved. The repetitive tasks done by humans in the shipping industry can be delegated to autonomous systems.
Research done by Allianz shows that 75%-96% of maritime accidents happen due to human error. Semi and fully automated systems can help humans make better decisions, analyze the data from the ship’s sensors efficiently and help make our oceans remarkably safer.
Autonomous systems can help reduce shipping costs significantly. Estimates indicate that, in general, crew-related expenses amount to 30% of the total budget in the industry. Along with reducing the personnel and associated costs of provisions, insurance, etc., the autonomous systems can also make the ship’s fuel usage more efficient.
SEA-Kit has developed a vessel named Maxliner that is fully autonomous that requires minimal human intervention. This ship does not have a human crew as it navigates autonomously. This vessel is equipped with several drone boats and submarines, which can perform various tasks. This kind of tech opens immense opportunities.
Challenges
The rapid innovation in autonomous shipping also comes with a slew of questions. The main concern is the potential unemployment of countless employees when ships can function without a crew and even do most maintenance work using robots. But these fears are misplaced, as projected by a report from the International Chamber of Shipping (ICS).
Most estimates predict that automation will create more jobs in the shipping industry. These can range from highly skilled personnel to manage the routes, remote pilots, seafarer officers, etc. So, automation is likely not going to eliminate jobs. Instead, automation is going to alter the nature of work in the shipping industry. Only time will tell how this will transpire.
One of the biggest challenges faced by future of autonomous ships will be that they need to work well with manned vessels. They need to learn to account for the variability of human decision-making and adjust their course, speed, and general navigation.
Autonomous ships are improving rapidly. However, it will take a while before these ships can navigate narrow and complex waterways like the English Channel. Initial test cases done are carefully controlled, but for a future of waterways filled with autonomous vessels – we will need to wait a bit longer.
Also, most autonomous ships in the immediate future will not be fully automated. The semi-autonomous ships will be just as prone to human error as any fully human-controlled vessel. The shore management of semi-automated and remotely controlled ships will still be prone to error in human decision-making.
The future of autonomous shipping
Overall, the maritime industry is about to experience a revolution in the coming years. While other technologies like AI, Machine Learning, and data analytics can refine the industry processes, automation will take the central stage and steer the industry to its future. The autonomous shipping industry will grow at a CAGR of 9.3% from 2020 to 2030, reaching a market size of over 14 billion over the next decade. But this future will also involve humans coexisting with the algorithms. Better regulation, planning, and execution of maritime robotics will ensure that the shipping industry will thrive.



Leave a Comment