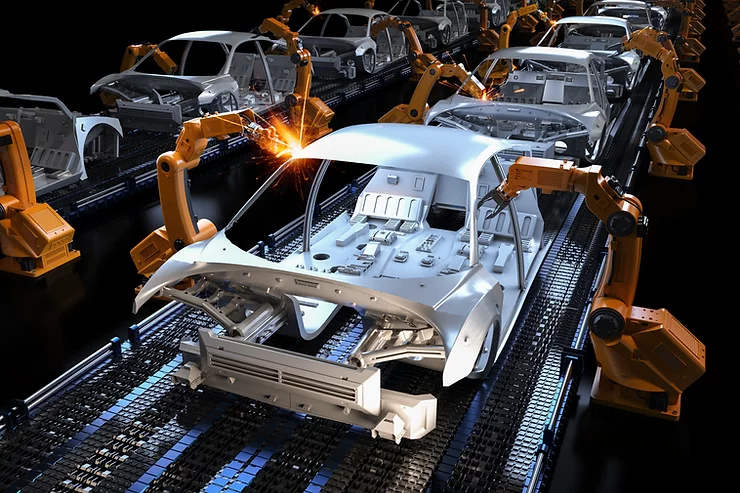
Collaborative Robots in the Automotive Industry
The last big technological advancement in the automotive industry was Henry Ford’s invention of the assembly line in 1913. Over a century later, it is now time for another tech revolution to take place, and this time, robots will take the lead.
What are Collaborative Robots?
Collaborative Robots, or Cobots, are essentially robots that work together with humans in order to optimise the workflow. They often come in the form of pre-coded arms which fit right into the existing assembly line and take care of the more labour intensive or health-damaging tasks.
With the complexity of the vehicles increasing and an ever-growing need for adaptable machinery, collaborative robots could not have come sooner. They provide a means for automotive factories to implement expensive robotic solutions that are scalable among all of the company’s products – the ones existing today, and the ones to come in the future.
Generally, there are three main types of collaborative robots: Robotic Arms, Drones, and Exoskeletons.
Robotic Arms
One of the most fundamental robotic structures is robotic arms. They are versatile and highly adaptable to any task. This is what makes them the perfect collaborative robot for integrating into an assembly line.
The key to a robotic arm’s versatility is the degrees of freedom it has. These allow the arm to perform almost any task without external assistance. What makes an arm multifunctional is the ability to change its tool heads. An arm’s tool head can be anything from a laser cutter to a suction cup. These tools, paired with the degrees of freedom, can accomplice almost anything around an automotive factory.
Universal Robots is a company that creates robotic arms for assembly line integration in automotive factories. They have arms with varying degrees of freedom, as well as functionalities. These arms can be programmed to do carry out any and all tasks that can be cast into code. Automation companies such as Ford have sensed the way the wind is blowing and already invested in these collaborative robot arms.
Drones as Collaborative Robots
Along with assembly line integration, collaborative robots can also be used in inspection and surveillance within a factory setting. The menial, yet important, job of surveillance currently occupies a significant amount of the workforce and can be easily automated with drone technology and computer vision.
Drones are already being used in many industries as inspection machines, and the automotive factories are quickly catching onto the trend. Drones can be programmed to fly in a search pattern around the factory floor and identify problems through an ML trained camera. Moreover, they help keep the workers safe by flying through the pipes and spotting signs of damage, such as cracks or corrosion.
Many major car manufacturers, such as Audi and Ford, have already started using drones are collaborative robots in their factories for doing all sorts of things. They are used for inspection, package delivery from one end of the factory to another, and even to remotely hand out car keys during the pandemic. In terms of the automotive industry, drone technology is just getting started.
Exoskeletons
Despite the giant recent advancements in robotics within the automotive industry, there are still parts of the assembly that cannot be replaced by robotics. These are often parts that are labour intensive and highly repetitive, not to mention risky.
Exoskeletons can solve this problem. This wearable technology is essentially a robotic bodysuit that can help the wearer with various tasks. They were originally invented to aid the old and the disabled with general tasks such as walking, however, the automotive industry is finding a new use for this technology. Exoskeletons are used to enable factory employees to be able to lift heavy loads and complete repetitive tasks with added precision. Their strong shells also protect the workers from injury.
ULS Robotics, a Shanghai-based company, is a pioneer in this technology. Their current design enables the workers to lift 44 extra ponds of weight and has 6-8 hours of battery life. Their exoskeletons are currently being tested by large automakers such as Hyundai, Ford, and General Motors.
Why Collaborative Robots?
Many would see collaborative robots as replacing human jobs, however, one of the biggest advantages of these robots is that they are programmed to do the highly repetitive and often dangerous tasks around an automotive factory. The aim is to keep humans safe and occupied at non-menial jobs.
The automotive industry is an ever-evolving market. Automobiles have come a long way and have a long way to go yet. In this market, a large concern is that of scalability. Will the technology implemented today still be useful tomorrow? With collaborative robots, the answer is yes. Since these robots are very simple, universal hardware devices, they can be programmed and modified for future products.
Another large advantage of collaborative robots is that they provide scalability and reliability at no additional cost. Since these robots are made for precision, there is no room for error in the process. As vehicles get more and more complex, these robots provide the tools with which this advancement can continue.
Upcoming Cobots
Cobots are just getting started in the auto industry. Although this technology is still in its research phase within the robotics labs of major automakers, we are already starting to see some of it come into the light.
Robotic arms are well on their way to replacing almost every repetitive task within the factory. As more of the technology is perfected within the research labs, it is expected that we will see these arms working hand-in-hand with humans in order to complete some of the most arduous tasks. Drone technology still has much to do with the automotive industry. From in-depth product inspection to becoming a flying toolbox for the factory floor, drones are certainly making their way into the factories.
Out of all the technologies discussed, exoskeletons are the most underdeveloped and perhaps the most important of all. It is hard to predict where this wearable technology will go, however, it is certain that it will be one of the next major advancements in the industry.



Leave a Comment