Lidars Vs Radar for autonomous vehicles: Analyzing the pros and cons
Lidars Vs. Radar for autonomous vehicles: Analyzing the pros and cons
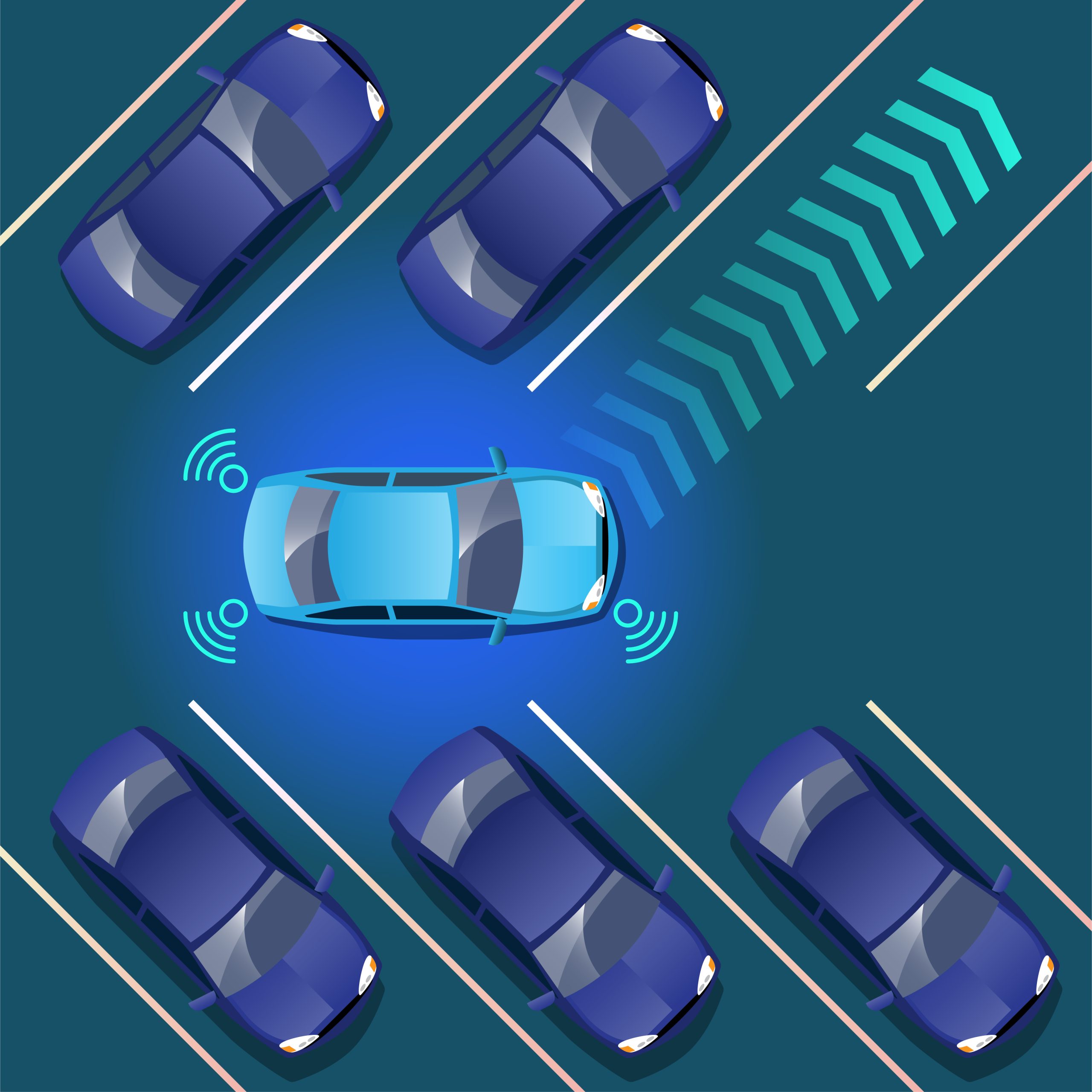
Autonomous cars are becoming increasingly intelligent, independent, and safer. They can communicate with other cars and infrastructure, making decisions based on real-time data. These cars come equipped with sensors and cameras that allow them to detect and avoid obstacles and park themselves. LiDAR and RADAR are two of the most common sensors used in autonomous vehicles.
LiDAR uses light pulses to measure distance and emits tens of thousands of laser pulses every second, which are processed into information by advanced algorithms. Valeo is a French technology firm that specializes in computer vision and LiDAR technologies. The Valeo third-generation LiDAR sensor system incorporates a wide field of vision and twenty-five times per second detection. It whips out long-range detection on the road, covering more than two hundred meters. The LiDAR system’s ability to create three-dimensional maps is also helpful in differentiating between cars, pedestrians, trees, people, and other objects. Additionally, the system can calculate and share details of an object’s velocity in real time.
RADAR emits radio waves and then detects reflections from nearby objects. By analyzing the reflections, the RADAR system can create a map of the surrounding area, which the autonomous car can use to navigate. Additionally, RADAR can operate in all weather conditions, making it a reliable tool for autonomous cars that need to be able to drive in all types of weather. A US-based firm called Spartan Radar develops radar technology with improved environmental perception capabilities. The company’s technology is based on advanced signal processing and machine learning techniques, which allow it to detect and track objects in complex environments with high accuracy.
Accuracy | Lidars Vs. Radar for Autonomous Vehicles
The image processing in LIDAR is better than RADAR for several reasons. LIDAR provides higher-resolution images, which makes it easier to identify objects. LIDAR’s superior image processing is due to its use of laser beams, which have a much shorter wavelength than radar waves. Shorter wavelengths also allow LiDAR systems to detect smaller targets and create 3D images of them.
Furthermore, LIDARs can scan greater distances and can respond more quickly, as compared to RADARs. Google’s Waymo self-driving car technology relies heavily on LIDAR. Waymo’s LIDAR technology can detect road works, parked cars, and hand signs from a cyclist to provide safe and accurate driving assistance. Waymo’s LIDAR system is so sophisticated that it can detect pedestrians, figure out what direction they are facing and in which direction they will walk, and provide a smooth ride for the rider. RADAR, on the other hand, is less precise and has a shorter range. It can only detect objects that are nearer to the vehicle.
Versatility | Lidars Vs. Radar for Autonomous Vehicles
RADAR systems are more versatile and provide more accurate measurements under extreme conditions, as compared to LIDARs. For example, Navtech’s high-resolution 360° long-range radar can detect rain, hail, snow, and fog during the day or at night. It provides a wide operating range and can gauge the amount of precipitation and its location. The 360° radar design allows it to monitor the entire horizon, regardless of weather conditions. Since RADAR has no mechanical moving components, it is less susceptible to dirt and can function in a variety of harsh environments.
LIDARs do not perform well under extreme conditions. This is so because fog, rain, and snow distort light waves, which are used by LIDAR to estimate distance. RADAR, which uses radio waves to measure distance, is not as easily distorted as light waves. Though some LIDAR systems, like those made by Innoviz, are resistant to harsh weather elements including high temperatures and humidity, RADAR systems are often far more effective in harsh environments.
Affordability | Lidars Vs. Radar for Autonomous Vehicles
RADARs are less expensive than LIDARs, which is why they are utilized more frequently. Radar is a lot cheaper to produce than LIDAR and just needs a basic transmitter and receiver. However, LIDAR needs a strong laser and complex optics. Also, LIDAR systems must be manufactured with greater precision and need to be very carefully aligned.
Depending on the brand and functionality, RADAR sensors for driverless cars can cost between $100 and $1000. Velodyne, a leading manufacturer of lidar sensors, has recently announced the release of a new $100 sensor. The new sensor is based on Velodyne’s proprietary VLP-16 laser scanning technology, which uses sixteen lasers to create a 3D map of the environment.
The sensor can detect objects at a range of up to one hundred meters, and can be used in a variety of settings, including urban and rural areas. Velodyne’s new sensor is a breakthrough in the autonomous vehicle industry and has the potential to greatly reduce the cost and improve the performance of autonomous vehicles. On the other hand, LIDARs can cost up to $75000. Though Waymo has successfully lowered the price to $7500, they are still not as cheap as RADARs.
Ideal LiDAR & RADAR Use Case Scenarios
RADAR systems are exceptional in monitoring collisions and cross-traffic. However, RADARs cannot capture the breadth of information that LiDAR systems perceive. Due to this restriction, objects may be misidentified or, if they are extremely small, may not even be detected. LiDAR systems can capture large volumes of data. The ability of LiDARs to image terrains at high-precision levels makes them the preferred choice for features like emergency brake assist and pedestrian detection. Gaps in the land that are difficult to navigate are also easier to navigate with LiDAR, which has a wider field of view.
LiDAR and RADAR technologies are sometimes combined to provide better results. Sensor fusion is a technique used in autonomous vehicles to combine data from multiple sensors to provide a complete picture of the surroundings. This technique uses LIDAR to produce a 3D map of the surroundings and RADAR to detect objects in the route of the vehicle. It allows the car to make better decisions and navigate more safely.
The Future | LiDAR & RADAR
A vast majority of autonomous vehicle manufacturers believe that LiDAR systems are the future of the autonomous vehicle industry. However, there are a few others who believe the opposite. For example, Tesla has developed its own RADARs and cameras instead of LiDARs. Tesla’s system is less expensive, and they believe it to be just as effective as LiDAR. However, many manufacturers are already using LiDAR systems in their prototypes and testing vehicles, and this trend will continue.
As both LiDARs and RADARs have pros and cons, it often makes sense to use a fusion of the two technologies. Many manufacturers including Audi, BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Volvo, and Ford are researching sensor fusion technology and will continue to do so in the coming years.
RADAR and LIDAR sensors have come a long way in recent years, and they are only going to get better in the future.



Leave a Comment