Robotaxi: The Future of Ride-Hailing
Robotaxi: The Future of Ride-Hailing
According to a recent study, the people of the United States alone spent 89 billion hours behind the steering wheel in 2019,
Averaging 59 minutes per driver every day.
People would have a slightly higher standard of living if this time were spent on more productive activities.
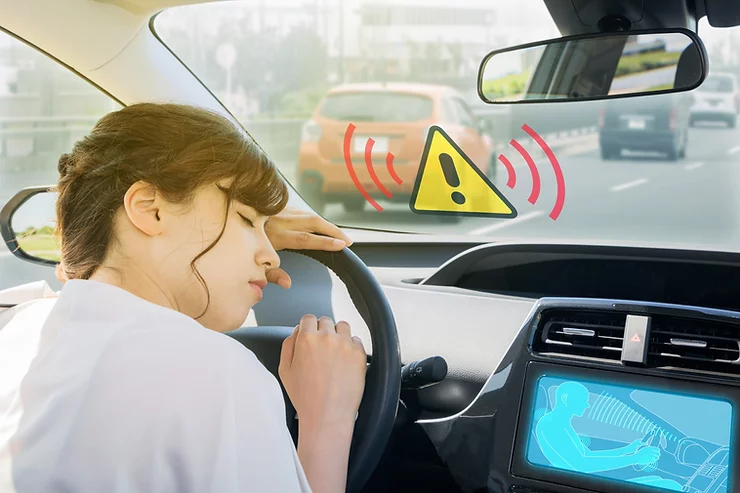
Another study confirmed that 96% of car accidents across the country happen due to human error.
In order to save driving time and offer riders a safe journey.
The auto industry is shifting towards an autonomous ride-hailing future.
Front Runners in Robotaxi Service
Waymo began its journey as a self-driving car project in 2009 and founded itself as a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. several years later.
The google spin off’s Robotaxi fleet roughly totals 600 vehicles, the majority of which are converted Chrysler Pacificas, of which 300 are currently operational.
Although the majority are level 4 autonomous vehicles, the company is unwilling to disclose the number of entirely driverless vehicles on the road today.
Waymo One – Waymo’s fully autonomous public ride-hailing division – is currently available in the East Valley of Phoenix, Arizona, including Chandler, Gilbert, Mesa, and Tempe.
The company runs the Waymo Trusted Tester program as a part of a new pilot program in San Francisco, totaling 100,000 miles of driving each week.
This research-focused program allows a few customers to experience the ride and share their feedback with the company.
It also has brought its self-driving car to New York to map the entire city for the first time. Waymo intends to eventually begin its journey in France and Japan.
The purpose of the firm is to break the technological barriers to bring a safe and comfortable Robotaxi service to customers worldwide.
Baidu
Baidu, a Chinese corporation best known for its search engine service, announced the debut of its apollo project to develop autonomous vehicles in 2017.
It quickly entered the global robotaxi race due to its accelerated investment in AI development via implementation of Platform Business Group (PBG- a synergy of multiple giant tech companies across China) strategy since 2016.
Since then, it has made over 500 self-driving automobiles.
The company has been conducting trials of self-driving cars since the beginning of last year in 23 cities, including Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou.
And Chongqing and is now aiming to reduce the price of its planned fifth-generation autonomous vehicles.
The perception layer involves the use of expensive LIDAR to map high-precision 3D spatial coordinate information, which increases the production cost.
Therefore, the company, along with another conglomerate, invested $150 million in Velodyne, a company well-known for LIDAR manufacturing, to intensify its research and reduce the cost of sensors.
Additionally, the organization seeks to reduce noise from point cloud data in bad weather or other specific conditions that are anomalous compared to the ideal one.
The company aims to expand its ride-hailing service to 65 cities by 2025 and 100 cities by 2030.
It has formed partnerships with several domestic and western auto manufacturers to build 3,000 Robotaxis within the next three years.
Cruise
Cruise, a division of General Motors, has also laid out its strategy for competing in this race at full throttle.
It was granted permission by the city authority to provide free rides in the San Francisco area of California.
However, the firm is currently seeking authorization from the authorities to commercialize its ride-hailing service.
The company is also working to improve its advanced driver-assistance technology.
The system is susceptible to software bugs since it requires fusion and processing of huge chunks of data from multimodal sensors and further actuation based on the analysis.
Therefore, it exhibits symptoms like system hangs, crashes, lane position and navigating errors, localization errors, traffic light processing errors, etc.
Researchers and engineers are scrupulously analyzing these characteristics of software and trying to develop AV bug detection to ease this process for the future.
Unlike the retrofitted Chevrolet Bolt, which is presently operational as a robotaxi, Cruise unveiled Shuttle Origin last year.
It intends to begin the series production of Shuttle Origin by the following year. The company also plans to establish its first overseas unit in Dubai.
The middle-eastern city authorities have agreed with the company, allowing on-demand ride-hailing service by 4,000 Cruise Shuttle Origins on the road by 2030.
AutoX.ai
AutoX.ai established itself as a worthy competitor both in the United States and China after its inception in 2016.
Since earlier this year, it has been operating its fully driverless autonomous vehicle in the Pingshan district of Shenzhen Megalopolis (65 square miles).
After ten months of operation, it has expanded its commercial service throughout the Megalopolis area.
It is now testing its driverless Robotaxis in California following approval by the state’s Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV).
The company intends to install 28 automotive-grade camera sensors capable of generating more than 200 million pixels per frame 360 degrees around the car.
However, the behavioral safety of its robotaxis is not sufficient yet.
Therefore, it expects to integrate NVIDIA’s end-to-end self-driving architecture to achieve deep-neural-network (DNN)-based precise steering angle verification.
The company has partnered with Spark Connected—a manufacturer of wireless power technology—to integrate wirelessly powered sensors into its robotaxi fleet.
It expects to bring Robotaxis into high-traffic areas of China and the US in the upcoming years.
Pony.ai
The Toyota-backed company Pony.ai launched its first robotaxi service, PonyPilot, in December of 2018, allowing passengers to hail self-driving cars via the PonyPilot+ application.
In collaboration with Luminar, a recognized manufacturer of automotive LIDAR and software packages, the company successfully established operations in Guangzhou, Beijing, Irvine, and Fremont, California.
In comparison to conventional LIDAR systems, which may require 64 lasers and 64 receivers or more, PonyPilots now use a single laser and a single receiver to rapidly scan the field of view.
The company is evaluating the benefits of solid-state LIDAR over mechanical scanning, as the moving parts and complexity of mechanical scanning result in high costs, even at large manufacturing volumes, and pose a risk of failure in rough driving environments.
It is the only self-driving firm with a fleet of more than 200 autonomous vehicles operating in five domestic and international cities.
The company plans to set out automotive-grade production of autonomous vehicles in 2023, lowering the production cost while expanding into new cities.
Where is the Robotaxi Service heading?
There are still numerous obstacles to overcome before the Robotaxi hailing service becomes a regular phenomenon.
They are highly vulnerable to hacking due to their connectedness with remote operators, other vehicles, and nearest infrastructure, which has become a major concern for industries.
Additionally, real-time response is still not as fast as projected due to insufficient bandwidth, speed and computing power.
Industries are placing bigger premiums on research and development than ever before to address these concerns.
They are collecting data from several cities regarding probable difficult circumstances and feeding these data to machine learning models to ensure safer travel for passengers.
It is only a matter of time before this technological marvel enables us to ride more affordably and safely.