The future of 5G on Autonomous Vehicle
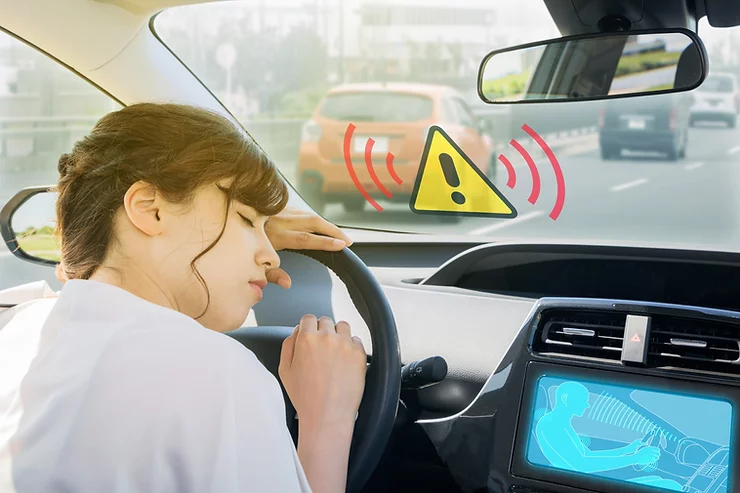
LG U+ and Hanyang University have recently (in mid-March 2019) tested an autonomous driving car with its 5G mobile communication commercial network. This was the first time for Seoul to test a 5G commercial network based autonomous vehicle. This is not completely surprising as South Korean telecom companies have been at the forefront of advancing mobile communication technology. But, this is a harbinger of the future of connected, autonomous vehicles!
Hanyang University’s Automobile Electronic Control Laboratory (ACE Lab) was involved in the project and the test vehicle completed an 8 km stretch from the Seongsu-dong Han River project headquarters in Seoul. The vehicle used had level 4 ‘advanced autonomous driving’ technology installed and the potential enhancement to autonomous driving using 5G was being implemented. The test vehicle sent information about an accident on its way to the control center through the 5G network and the control center informed the new optimal driving route to the vehicle back. It also streamed high-quality 5G video and VR content in the car without interruption for the entertainment of the passengers. This suggests that 5G would not only enhance the autonomous driving capability of cars but also help in creating a new media consumption channel through high fidelity video streaming.
5G is still in its test phase and the standard itself is yet to be finalized. There have been concerns with the involvement of Huawei in the 5G advancement from major Western countries in recent times. One such example happened in New Zealand in the same time period where Spark and Ohmio Automation tested a 5G connected and autonomous shuttle for constrained environments like University campuses, airports, etc. in New Zealand. But, the 5G trial was not well received by New Zealand’s Government Communications Security Bureau (GCSB) which passed a draft decision inhibiting the use of any 5G technology from Huawei in the implementation. The Australian government had already passed such a decision a few months earlier. But, other communication technology firms like Qualcomm are also testing their 5G equipment and therefore these issues may not have a significant impact going forward. But, the standardization itself may have issues as Huawei is an important member of the 3GPP alliance.
A significant impact of 5G on autonomous vehicles would only come with the 5G V2X standards. The cellular V2X standard has backing from most major automotive companies and telecom players but Toyota and a few others are still backing the traditional DSRC protocol for V2X communication. There is also a 5G Automotive Alliance for determining standards with most automotive, telecom and communication equipment players as members but this too does not have Toyota as its members. This has hampered the rapid adoption of the technology.
5G V2X as promised could deliver substantial improvements in autonomous driving. This could mean the low latency communication network could easily update the HD maps needed for autonomous driving real-time. This would substantially reduce the very high requirement of the vision sensors on the vehicle currently. The vehicles could even talk to each other which could act as an additional sensor in itself while also updating the local issues like accidents, traffic jams, etc. across the vehicle network in near real-time. It could also mean that the traffic signals could be managed more effectively and the traffic flow itself be managed in a much more optimized way. The standard toll payments, parking-related tickets could also be completely automated.
But, this still seems a moonshot dream as the players have to agree on the standards while trade war and political pressures loom large on the future of 5G, especially for the automotive industry.
To deep dive and stay continuously updated about the most recent global innovations in Autonomous Vehicles and learn more about applications in your industry, test drive WhatNext now!



Leave a Comment